Pests reduce 20% to 40% of world agricultural production.
Insect short life cycle and high reproduction rate contribute to the development of resistance to insecticides, as well as the high frequency of use of these products.
Different mechanisms of action interfere in the sensitivity of these pests to chemical compounds: behavioral changes, reduced penetration into the insect cuticle, increased capacity for detoxification metabolism and biological modifications in insecticide active sites.

Fernando Gava, President of IRAC Brasil
AgriBrasilis interviewed Fernando Gava, Trait Development Country Manager at BASF, and President of IRAC – Brazil. Gava is agronomic Engineer and Master in Plant Production from the State University of Santa Catarina,
Insecticide Resistance Action Committee (IRAC) is a group of technicians experts in plant health with the objective of preventing or delaying the development of resistance in insects and mites. The Committee is dedicated to extend the effectiveness of insecticides and acaricides in combating resistance.
AgriBrasilis – What are the foundations for Insecticide Resistance Management programs and how does IRAC work?
Fernando Gava – Insecticide resistance management programs are most effective when performed covering as much of the areas as possible. In the large growing scenarios in Brazil, this naturally means that integrated pest management and insecticide resistance management are not in the hands of just one individual. The benefits of implementing best pest management practices are most evident when farmers can coordinate and communicate activities through a resistance management program over large areas.
The basis for an efficient strategy for the Management of Insecticide Resistance are:
Plan ahead considering when insect control will be needed during the plant cycle, ensuring that a variety of insect control options are available.
Build a pest management plan for the crops, but also consider the pests that may transfer from one crop to another.
Make effective use of available insect control options using locally approved action levels for pest management.
Rotate insecticides with different modes of action to avoid resistance selection.
Always follow the recommendations of the seed breeders regarding the sowing of the refuge, insecticide leaflet dose and use of adequate application equipment.
Avoid parallel or sequential sowing of host crops of the same insect pests.
Since its creation, IRAC has been working on three basic projects: institutional, educational and research. The institution was conceived to present IRAC-BR to the scientific community, extension workers and farmers. The educational goal is to create technical-didactic material for the dissemination of issues related to resistance and implementation of management strategies. The research project aims to maximize efforts in order to monitor and develop specific work in the field of pest resistance to pesticides.
AgriBrasilis – Is it possible to predict or anticipate the action of pests in the field?
Fernando Gava – It is very difficult because of the interface with several factors, both biotic and abiotic. But we can work preventively to avoid the presence and development of pest resistance through the adoption of the set of good practices mentioned in the image below.
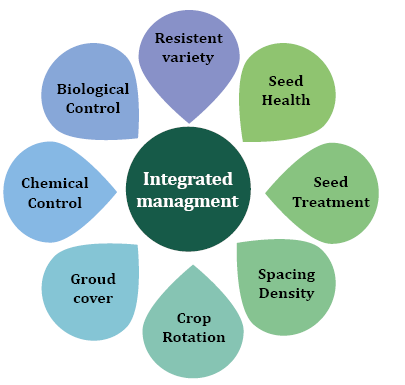
Integrated Pest Management best practices
AgriBrasilis – What are the causes for the emergence of resistance to insecticides?
Fernando Gava – Insecticide resistance can be defined as “an inherited change in the sensitivity of a pest or population that is reflected in the repeated failure of a product to achieve the expected level of control when used in accordance with the label recommendation for that pest (IRAC)”.
Resistance arises from the excessive use or misuse of an insecticide or acaricide against pests and results from the selection of resistant forms of the pest and the consequent evolution of populations resistant to that insecticide or acaricide.
AgriBrasilis – What are the main concerns related to specific products and resistance?
Fernando Gava – The following resistances (table below) have been reported in Brazilian insect populations. Those responsible for carrying out pest management programs should consult with local experts to determine whether products containing these insecticides are considered effective in controlling the target pests. In the lack of information about the insect’s susceptibility to these insecticides, give preference to alternative modes of action that are not affected by resistance.
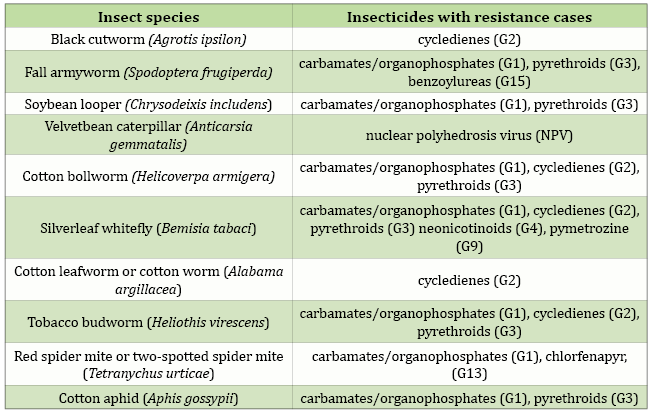
Reported cases of insecticide resistance
AgriBrasilis – Do biological products help to minimize the emergence of resistance?
Fernando Gava – No doubt they do. It is very important, especially in the case of insects, to adopt methods that help in handling them. Biological products bring diversity to the system and different modes of action compared to chemical insecticides, being an extremely important tool to enable the rotation of strategies.
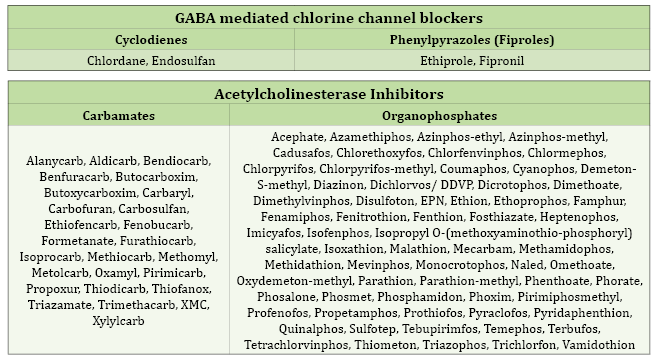
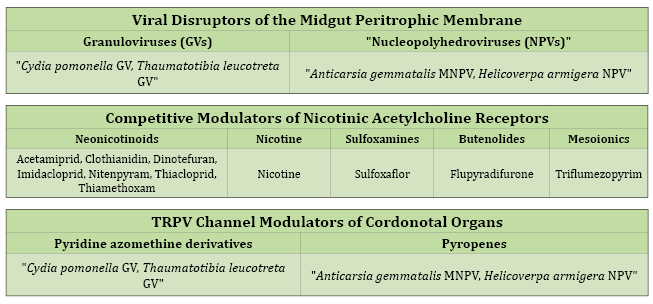
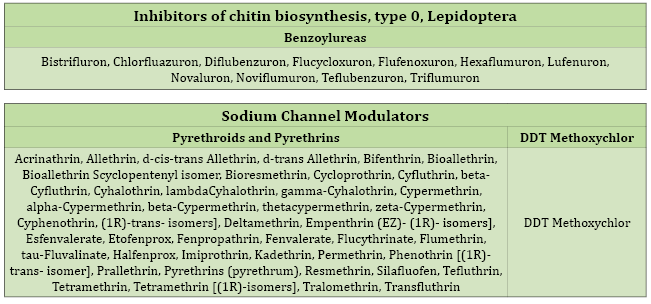
Additional information: Classification of the main insecticides and acaricides according to their mode of action and chemical group
This information helps in decision making in the field for the adoption of good agricultural practices in the prevention and management of pests in different agricultural crops.